BMG Entertainment case
Memorandum
To: Strauss Zelnick
Subject: BMG Entertainment
Date: Feb 1, 2011
At the end of the 20th century, BMG faced dramatic changes in the industry ignited by the Internet. This new technology emerged as new ways of recording and distributing music and as new marketing and publishing vehicles. This threatened to destroy the well established behemoth of media and record companies. Immediate steps should be taken to change the existing business model as well as to make substantial investments into Internet technologies.
Music downloads
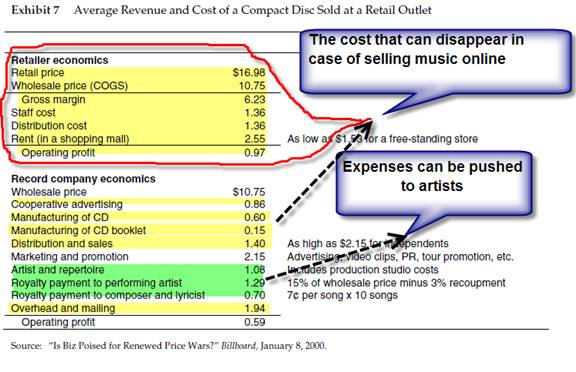
The market perception is that soon all music distribution will be happening online. Downloading entrepreneurs such as MP3.com and EMusic.com were unprofitable but significant interest was shown from market participants. MP3.com went through the IPO process despite the fact that most popular musicians were absent from the site. More than 90% of its revenue came from advertisements.
Music Piracy
Unauthorized copying of music caused the most concern for companies like BMG. However, an attempt to recover cost by taking in suspected piracy people would not be successful due to high legal costs and the low financial soundness of such people. Restriction on distribution tools for copying music files is also not possible. It makes more sense to make music more affordable. Customers would then be more willing to buy music versus copying it illegally. Piracy downloads can be seen as marketing expenses in this case.
Suggestions
Lower cost: Operating costs can be substantially lowered by eliminating manufacturing and distribution costs of CD and cassettes.
Service provider: BMG should become an Internet portal site for providing value and services for customers buying music and for musicians and composers. The risks of releasing new albums should be shifted to artists and composers. In return, musicians would be able to set their own prices for songs. BMG would then have to recover this cost later. BMG could provide a package of online tools to help singers to connect with appropriate composers.
Customer engagement: Develop more specialized sites based on user interests and different genres. Create lists of interested customers and notify them about new releases. These customers would likely buy new songs as soon as they became available. Distribute songs on a monthly subscription basis. Create customized sources of streaming music online thus attracting people to their websites. Also, make borderless, wide-ranging music libraries available online.
New products
With further development of Internet technologies, music videos will likely become more in demand. These music videos could then substantially replace regular music recordings.
New sources of revenue
BMG can leverage their industry knowledge, relationship and connections to participate in concert organization, marketing and promotions. They could also generate revenue by publishing advertisements on their websites.
Appendixes
| Unique Visitors to Selected Online Music ServicesMarch 2004
comScore Media Metrics |
||
| Unique Visitors(000) | ||
| Total Visitors to Selected Music Services | 11,249 | |
| MUSICMATCH.COM | 5,335 | |
| Roxio, Inc (Napster) | 2,567 | |
| ITune | 2,333 | |
| Listen.com Sites | 1,387 | |
| Walmart Music Store | 535 | |
| LIQUID.COM | 169 | |
Source: http://www.pewinternet.org/~/media/Files/Reports/2004/PIP_Filesharing_April_04.pdf.pdf